Health Consequences of Obesity
Obesity increases the risk of serious health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, sleep apnoea, and certain cancers. It also affects mental wellbeing, mobility, and overall quality of life.
The Hidden Dangers of Excess Weight
The health risks associated with obesity are often underestimated, yet the condition can lead to a wide range of serious and potentially life-threatening complications. As excess body fat accumulates, it places strain on nearly every system in the body, increasing the risk of chronic disease and reducing overall life expectancy. Below are some of the most well-established medical consequences of obesity:
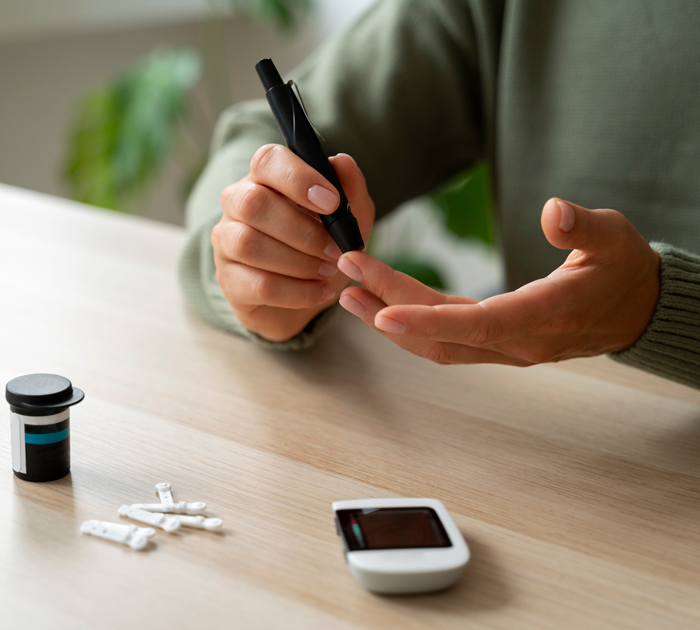

Obesity is one of the strongest risk factors for insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes.
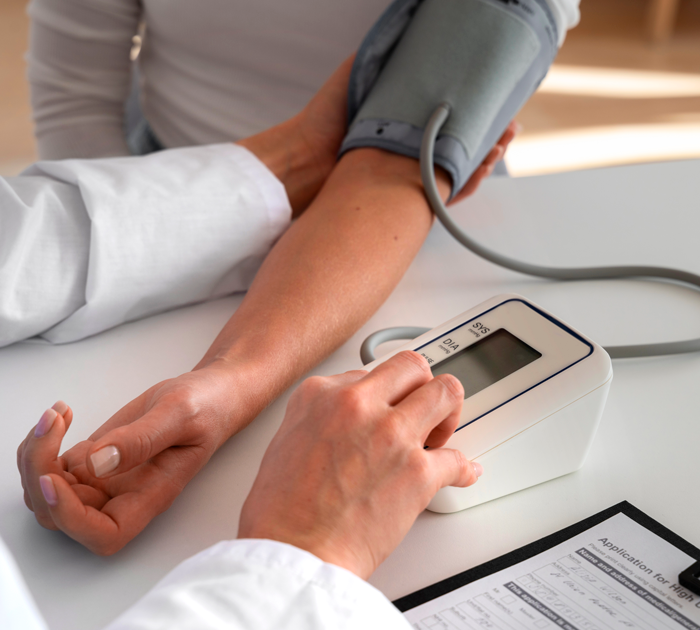
Excess fat increases vascular resistance, raising blood pressure and stressing the cardiovascular system.
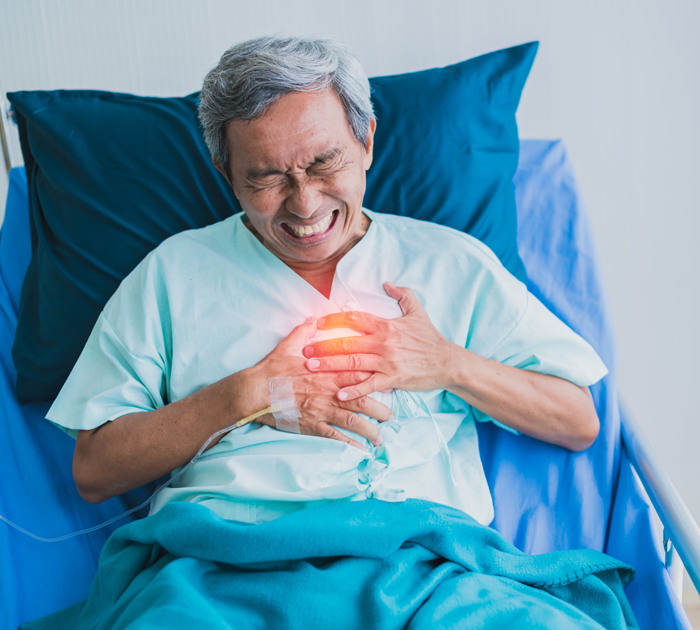

Obesity contributes to atherosclerosis, heart failure, and other cardiac conditions.

Increased blood pressure and cholesterol levels in obese individuals significantly elevate stroke risk.
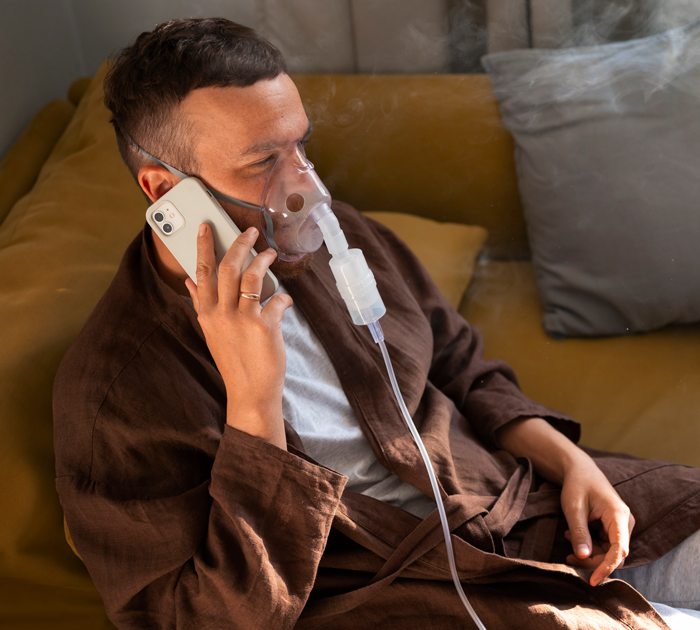

Fat deposits around the neck and airway can cause severe breathing interruptions during sleep
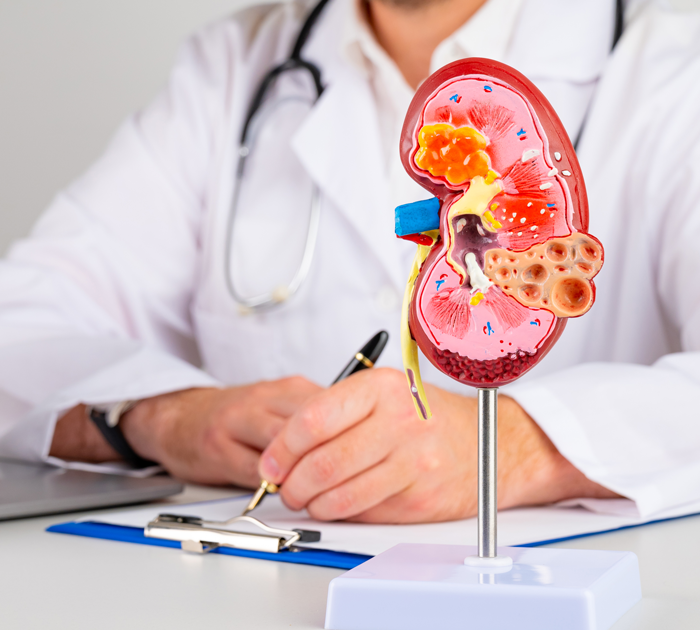
A growing concern in obese patients, this condition can progress to liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.

Obesity is an independent risk factor for chronic kidney disease, especially when combined with diabetes or hypertension.

Gallstones and gallbladder dysfunction are more common in obese individuals.
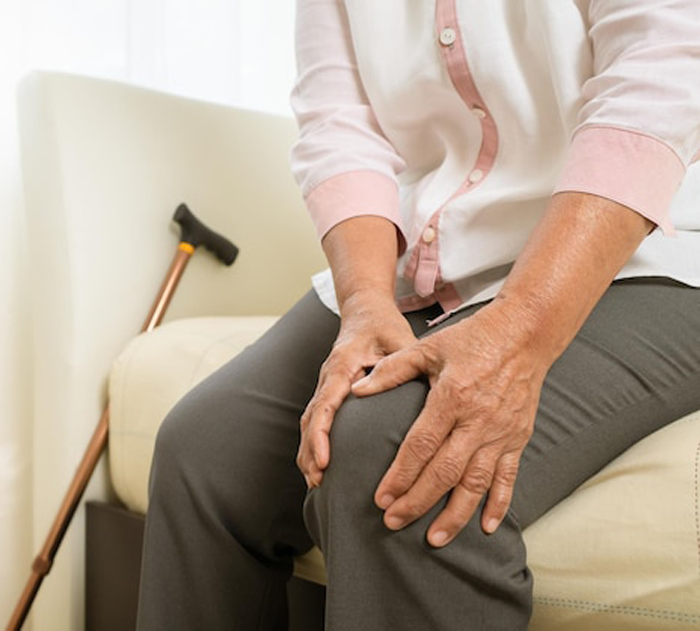
Excess weight places mechanical stress on joints, accelerating cartilage breakdown and joint pain.

Obesity has been linked to increased risk of several cancers, including breast, colon, endometrial, and pancreatic cancer.
